|
REGULAR POLYGON
A regular polygon is a polygon whose sides are all the same length, and whose
angles are all the same. The sum of the angles of a polygon with n sides, where n is 3 or more, is 180° × (n - 2)
degrees.
Examples:
The following are examples of regular polygons:

Examples:
The following are not examples of regular polygons:
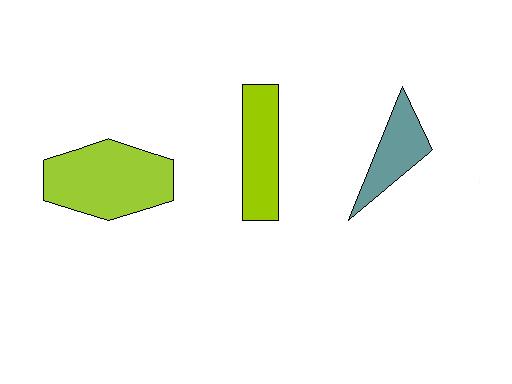
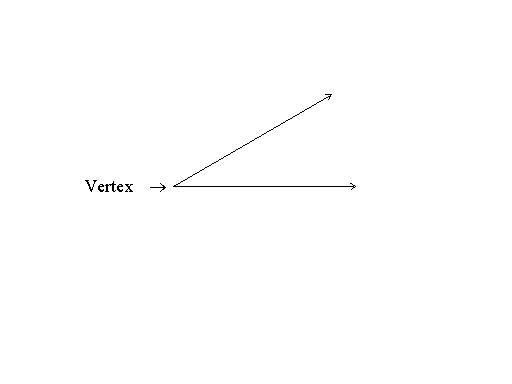
1) The
vertex of an angle is the point where the two rays that form the angle intersect.
2)
The vertices of a polygon are the points where its sides intersect.

TRIANGLE
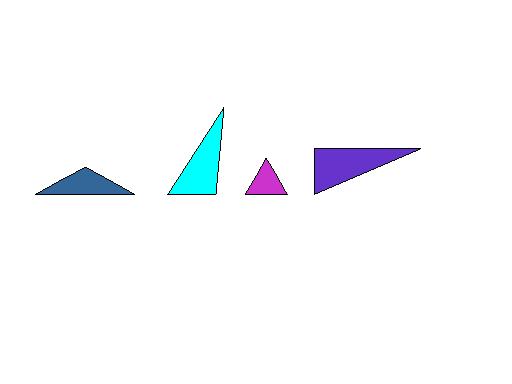
A three-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
Equilateral
Triangle Or Equiangular Triangle
A triangle having all three sides of equal length. The angles of an equilateral triangle all measure 60 degrees.
Examples:
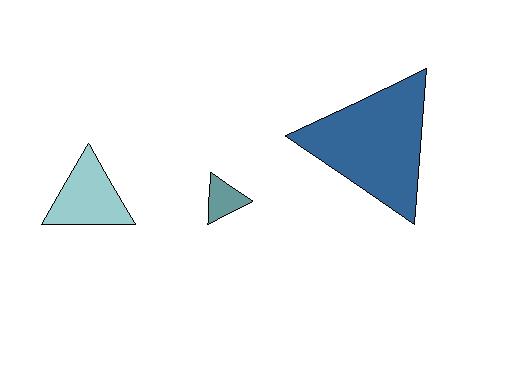
Isosceles
Triangle
A triangle having two sides of equal length.
Examples:
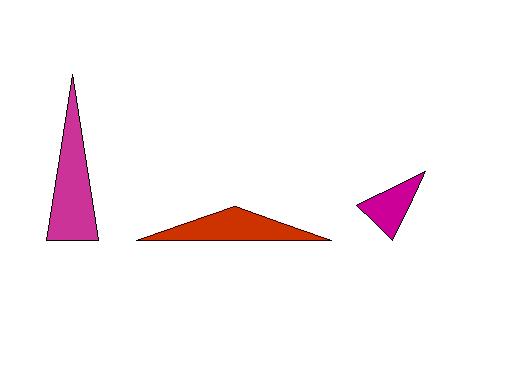
Scalene
Triangle
A triangle having three sides of different lengths.
Examples:
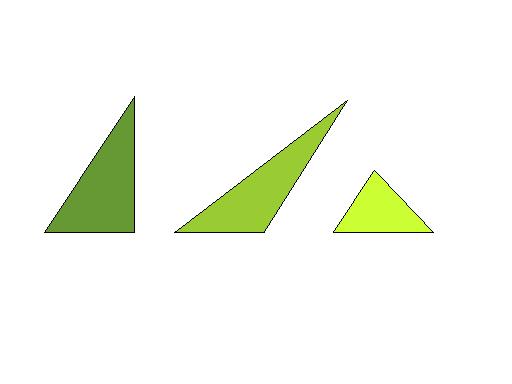
A triangle
having three acute angles.
Examples:
Obtuse Triangle
A triangle having an obtuse angle. One of the angles of the triangle measures more than 90 degrees.
Examples:
Right
Triangle
A triangle having a right angle. One of the angles of the triangle measures 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle
is called the hypotenuse. The two sides that form the right angle are called the legs. A right triangle has the special property
that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs equals the square of the length of the hypotenuse. This is known as
the Pythagorean Theorem.
Examples:
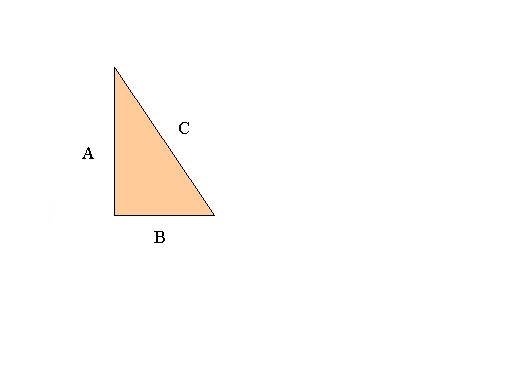
For the right triangle at the left, the lengths of the legs are A and B, and the hypotenuse has length C. Using the Pythagorean
Theorem, we know that A2 + B2 = C2.
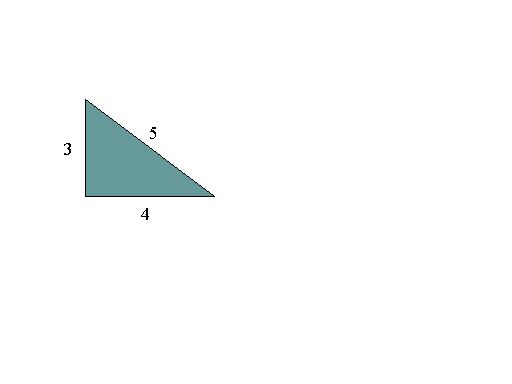
In the right triangle at the right, the hypotenuse has length 5, and we see that 32 + 42 = 52
according to the Pythagorean Theorem.
A four-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
Examples:
A
four-sided polygon having all right angles. The sum of the angles of a rectangle is 360 degrees. Examples:
Square
A four-sided polygon having equal-length sides meeting at right angles. The sum of the angles of a square is 360 degrees.
Examples:
A four-sided polygon with two pairs of parallel sides. The sum of the angles of a parallelogram is 360 degrees. Examples:
Rhombus
A four-sided polygon having all four sides of equal length. The sum of the angles of a rhombus is 360 degrees.
Examples:
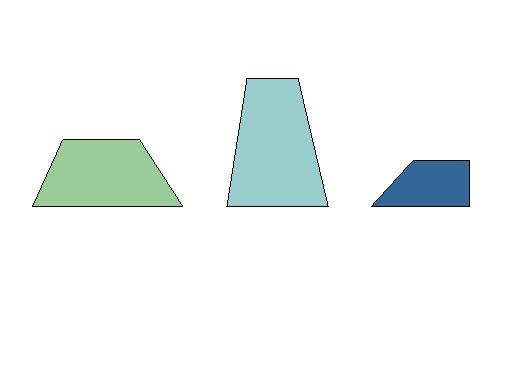
Trapezoid
A four-sided polygon having exactly one pair
of parallel sides. The two sides that are parallel are called the bases of the trapezoid. The sum of the angles of a trapezoid
is 360 degrees. Examples:
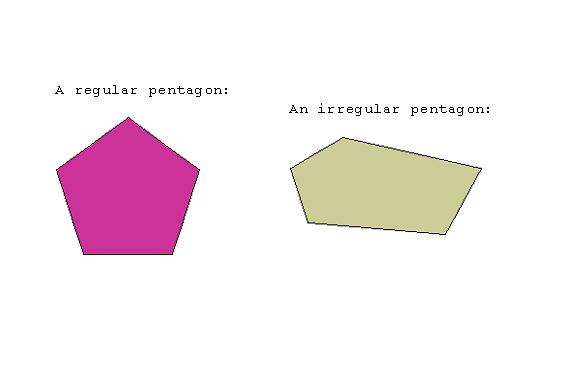
PENTAGON
A
five-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a pentagon is 540 degrees.
Examples:
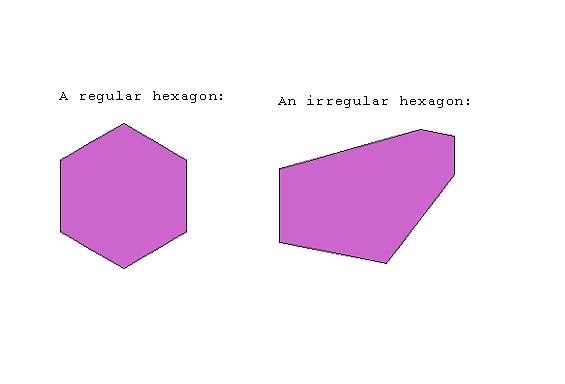
A six-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a hexagon is 720 degrees.
Examples:
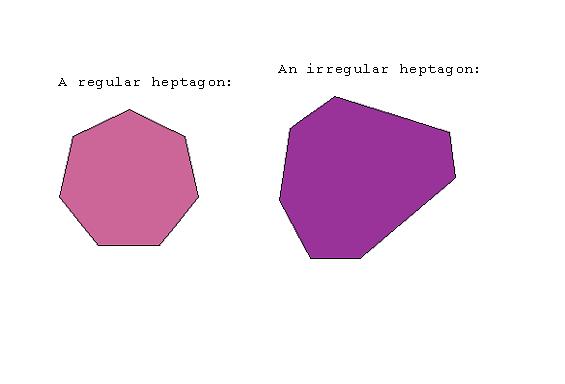
HEPTAGON
A seven-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a heptagon is 900 degrees.
Examples:
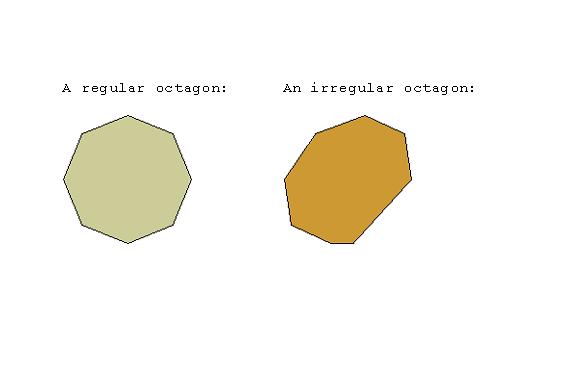
OCTAGON
An eight-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of an octagon is 1080 degrees.
Examples:
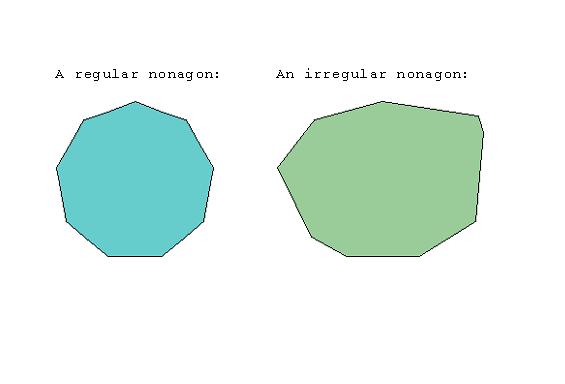
NONAGON
A nine-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a nonagon is 1260 degrees. Examples:
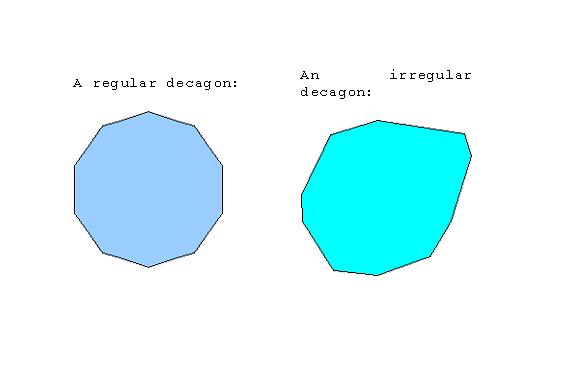
DECAGON
A ten-sided polygon. The sum of the angles of a decagon is 1440 degrees.
Examples:
|
